Nine out of ten CPGs using robotics are turning to the technology to alleviate struggles finding and retaining labor for mundane and repetitive tasks throughout the production floor, according to PMMI Business Intelligence's 2022 report "Robots and Cobots – An Automated Future."
Participating food manufacturers in particular are looking at robots and/or cobots to reduce their reliance on labor and achieve safer food handling. One packaging engineer manager at a large food company says in the report about a fifth of the company’s plants across North America use robots, “mainly for case packing and palletizing, and we’re continuing to invest where it makes sense to replace labor.”
The majority (78%) of CPGs using robots are also aiming for increased speed and productivity. “We envision cobots will have applications in secondary packaging to sort products to achieve faster throughput,” an engineering manager at a leading beverage company says in the report.
68% of CPGs use robots to achieve repeatable quality and consistent product handling. A manufacturing tech engineer for a large household products company says cobots can specifically help with “moving products from point A to point B and for applying the label to various sizes and configurations.” In a similar vein, 33% use robots to minimize waste and human error in production.
About half (51%) of CPGs using robots cited improving operator safety as a key draw, replacing tasks that might cause injuries such as packing and palletizing.
Other benefits of robots noted by CPGs included an increase in task accuracy, flexibility to perform multiple functions, optimal plant floor utilization, and a reduction in operating costs.
Adding robots to CPG production does have its drawbacks though. Over half (51%) of surveyed CPGs see an internal lack of capabilities as the primary reason impeding robotic implementations.
Those who noted internal shortfalls specifically cited a lack of internal engineering skills to integrate and service robots, difficulty identifying appropriate applications, and challenges with integrating the robots into existing lines. “Finding the right integrator can be key,” an engineering manager at a large pharmaceutical company says. Other internal concerns include insufficient floor space and a lack of dedicated time.
About a third (30%) of surveyed CPGs wary of implementing robots say total cost is a concern, noting unfavorable ROI and TCO estimates, the initial purchase cost, and installation, integration, and training cost.
A lack of functionality in current robot technology was also a concern. 22% of CPGs noted a need for improvements in the robot space including faster speeds, safer guarding, precise positioning, customization, flexible changeover, and handling dexterity.
“An ongoing challenge to deploying more robotics internally is the general understanding of how robots can contribute to the overall efficiency of a production line,” an assistant plant manager at a large pet food company said.
And finally, one out of 10 surveyed CPGs said a lack of support services kept them from integrating robots to production. Specific concerns included insufficient training to run the technology, and potential to lengthen lead times and availability through the switch.
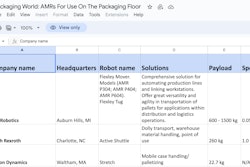
Source: PMMI Business Intelligence, 2022 Robots and Cobots: An Automated Future.
Download the FREE report below.